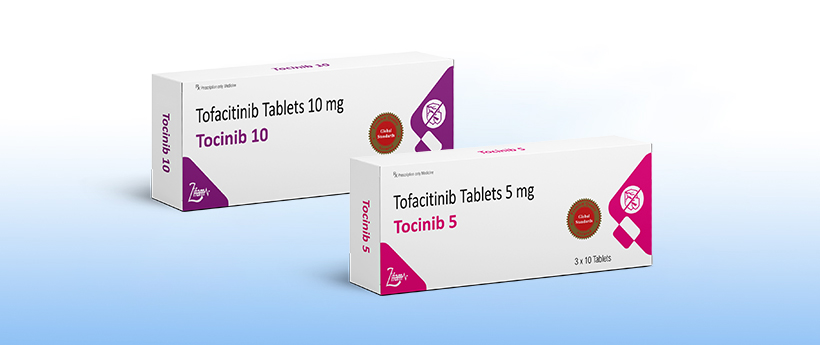
Tocinib 5 / 10
- ENG
- မြန်မာ
For the use of Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or Laboratory
Tofacitinib Tablets 5 mg
TOCINIB 5
COMPOSITION
Each film-coated tablet contains:
Tofacitinib…………….5 mg
Tofacitinib Tablets 10 mg
TOCINIB 10
COMPOSITION
Each film-coated tablet contains:
Tofacitinib…………….10 mg
Tofacitinib Extended-Release Tablets 11 mg
TOCINIB ER
COMPOSITION
Each extended-release tablet contains:
Tofacitinib…………….11 mg
1.DESCRIPTION
TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER are formulated with the citrate salt of tofacitinib, a JAK inhibitor.
Tofacitinib citrate is a white to off-white powder with the following chemical name:(3R,4R)-4-methyl-3-(methyl-7H-pyrrolo [2,3-dlpyrimidin-4-ylamino)-soXO-1 piperidinepropanenitrile, 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate(1:1).
The solubility of tofacitinib citrate in water is 2.9 mg/mL.
Tofacitinib citrate has a molecular weight of 504.5 Daltons (or 312.4 Daltons as the tofacitinib free base) and a molecular formula of C16H20N6OC6H8O7.
2.CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
2.1 Mechanism of Action
Tofacitinib is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor. JAKs are intracellular enzymes which transmit signals arising from cytokine or growth factor-receptor interactions on the cellular membrane to influence cellular processes of hematopoiesis and immune cell function. Within the signaling pathway, JAKs phosphorylate and activate Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription (STATs) which modulate intracellular activity including gene expression.
Tofacitinib modulates the signaling pathway at the point of JAKs, preventing the phosphorylation and activation of STATs. JAK enzymes transmit cytokine signaling through pairing of JAKs (e.g., JAK1/JAK3, JAK1/JAK2,JAK1/TyK2 JAK2/JAK2). Tofacitinib inhibited the in vitro activities of JAK1/JAK2 JAK1/JAK3, and JAK2/JAK2 combinations with ICs of 406, 56, and 1377 nM, respectively. However, the relevance of specific JAK combinations to therapeutic effectiveness is not known.
2.2 Pharmacodynamics
Treatment with TOCINIB was associated with dose-dependent reductions of circulating CD16/56+ natural killer cells, with estimated maximum reductions occurring at approximately 8-10 weeks after initiation of therapy. These changes generally resolved within 2-6 weeks after ‘discontinuation of treatment. Treatment with TOCINIB was associated with dose-dependent increases in B cell counts. Changes in circulating T-lymphocyte counts and T. lymphocyte subsets (CD3+, CD4+ and CD8+) were small and inconsistent. The clinical significance of these changes is unknown Total serum IgG, IgM and IgA levels after 6-month dosing in patients with rheumatoid arthritis were lower than placebo; however, changes were small and not dose-dependent. After treatment with TOCINIB in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, rapid decreases in serum C-reactive protein (CRP) were observed and maintained throughout dosing. Changes in CRP observed with TOCINIB treatment do not reverse fully within 2 weeks after discontinuation, indicating a longer duration of pharmacodynamic activity compared to the pharmacokinetic half-life, Similar changes in T cells, B cells, and serum CRP have been observed in patients with active psoriatic arthritis although reversibility was not assessed Total serum immunoglobulins were not assessed in patients with active psoriatic arthritis.
2.3 Pharmacokinetics
TOCINIB
Following oral administration of TOCINIB peak plasma concentrations are reached within 0.5-1hour, elimination half-life is about 3 hours and a dose- proportional increase in systemic exposure was observed in the therapeutic dose range. Steady state concentrations are achieved in 24-48 hours with negligible accumulation after twice daily administration.
TOCINIB ER
Following oral administration of TOCINIB ER, peak plasma concentrations are reached at 4 hours and half-life is about 6 hours. Steady state concentrations are achieved within 48 hours with negligible accumulation after once daily administration. AUC and C_ of tofacitinib for TOCINIB ER 11 mg administered once daily are equivalent to those of TOCINIB 5 mg administered twice daily.
Absorption
TOCINIB
The absolute oral bioavailability of TOCINIB is 74%. Coadministration of TOCINIB with a high-fat meal resulted in no changes in AUC while C, was reduced by 32%. In clinical trials, TOCINIB was administered without regard to meals.
TOCINIB ER
Coadministration of TOCINIB ER with a high-fat meal resulted in no changes in AUC while Cmax was increased by 27% and Tmax was extended by approximately 1hour.
Distribution
After intravenous administration, the volume of distribution is 87 L. The protein
binding of tofacitinib is approximately 40%. Tofacitinib binds predominantly to albumin and does not appear to bind to o-acid glycoprotein. Tofacitinib distributes equally between red blood cells and plasma.
Metabolism and Excretion
Clearance mechanisms for tofacitinib are approximately 70% hepatic metabolism and 30% renal excretion of the parent drug. The metabolism of tofacitinib is primarily mediated by CYP3A4 with minor contribution from CYP2C19. In a human radiolabeled study, more than 65% of the total circulating radioactivity was accounted for by unchanged tofacitinib, with the remaining 35% attributed to 8 metabolites, each accounting for less than 8% of total radioactivity. The pharmacologic activity of tofacitinib is attributed to the parent molecule.
3.INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Rheumatoid Arthritis
TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to methotrexate. It may be used as monotherapy or in combination with methotrexate or other nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
– Limitations of Use: Use of TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER in combination with biologic DMARDs or with potent immunosuppressants such as azathioprine and cyclosporine is not recommended.
Ulcerative Colitis
TOCINIB is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC).
– Limitations of Use: Use of TOCINIB in combination with biological therapies for UC or with potent immunosuppressants such as azathioprine and cyclosporine is not recommended.
4.DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
4.1 Important Administration Instructions
– Do not initiate TOCINIB/TOCINIB ER in patients with an absolute lymphocyte count less than 500 cells/mm², an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) less than
– ls/mm² or who have hemoglobin levels less than 9 g/dL.
– Dose interruption is recommended for management of lymphopenia, neutropenia, and anemia
– Interrupt use of TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER if a patient develops a serious infection until, the infection is controlled
– Take TOCINIB/TOCINIB ER with or without food
– Swallow TOCINIB ER tablets whole and intact. Do not crush, split, or chew.
4.2 Recommended Dosage in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Psoriatic Arthritis
Table 1 displays the recommended adult daily dosage of TOCINIB and TOCINIB ER and dosage adjustments for patients receiving CYP2C19 and/or CYP3A4 inhibitors, in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment or moderate hepatic impairment, with lymphopenia, neutropenia, or anemia.
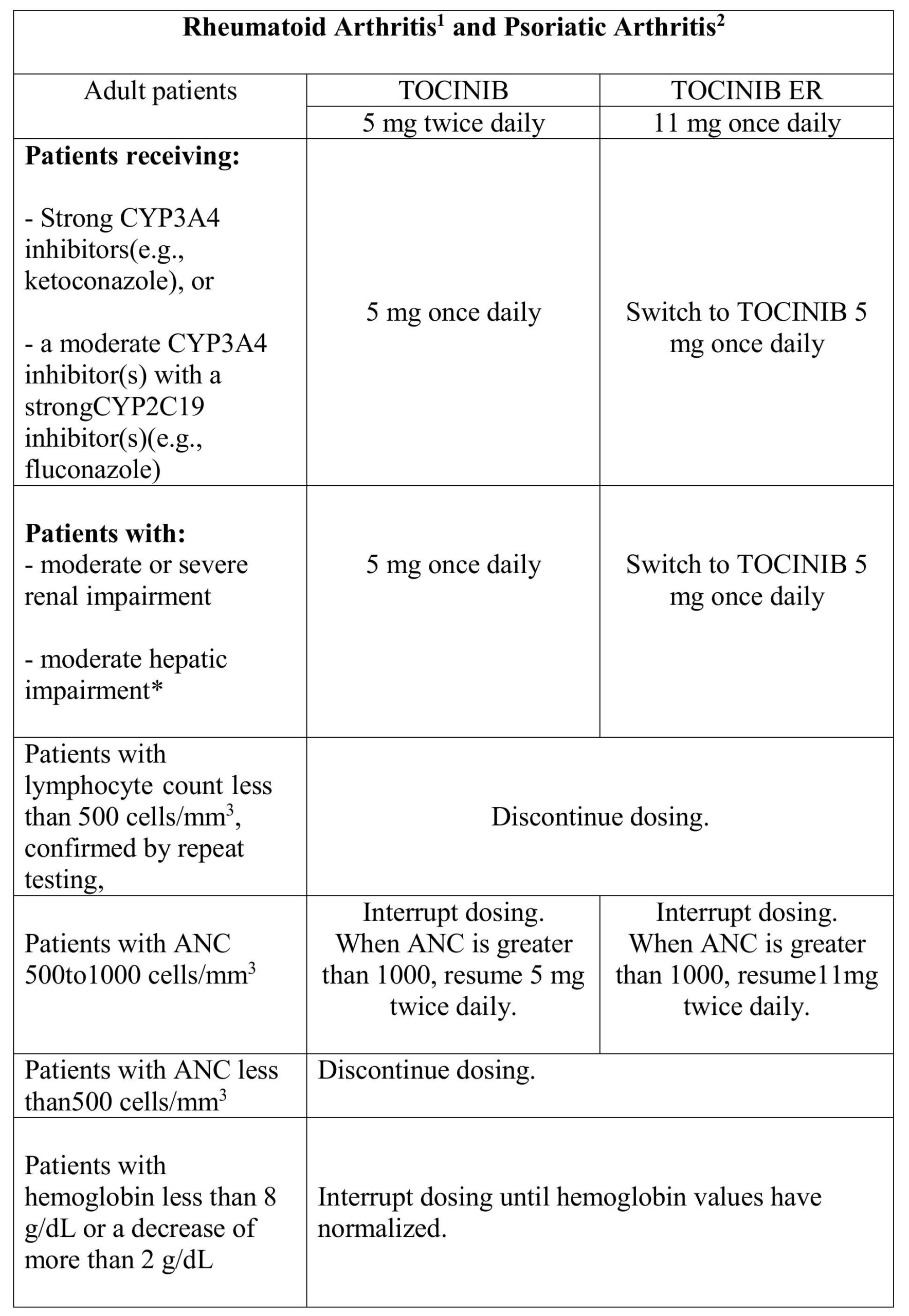
1TOCINIB /TOCINIB ER may be used as monotherapy or in combination, with methotrexate or other nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in rheumatoid arthritis.
2TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER is used in combination with nonbiologic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in psoriatic arthritis. The efficacy of TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER as a monotherapy has not been studied in psoriatic arthritis.
*Use of TOCINIB/TOCINIB ER in patients with severe hepatic impairment is not recommended.
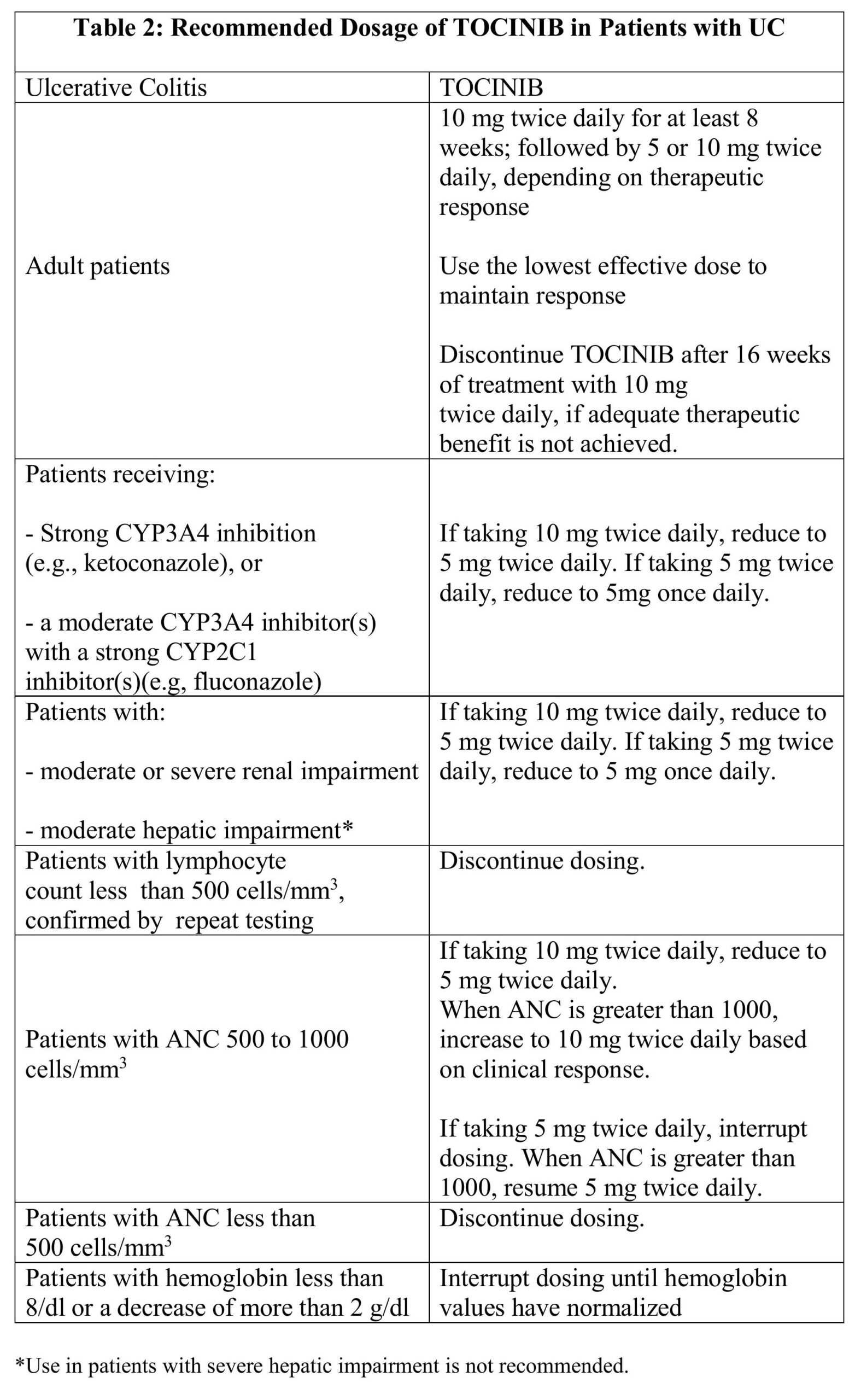
4.3 Recommended Dosage in Ulcerative Colitis
Table 2 displays the recommended adult daily dosage of TOCINIB and dosage adjustments for patients receiving CYP2C19 and/or CYP3A4 inhibitors, with moderate or severe renal impairment or moderate hepatic impairment, with lymphopenia, neutropenia or anemia.
5.WARNINGSAND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Infections
Serious and sometimes fatal infections due to bacterial, mycobacterial, invasive fungal, viral, or other opportunistic pathogens have been reported in patients receiving TOCINIB. The most common serious infections reported with TOCINIB included pneumonia, cellulitis, herpes zoster, urinary tract infection, diverticulitis, and appendicitis. Among opportunistic infections. tuberculosis and other mycobacterial infections, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, esophageal candidiasis, pneumocystosis, multidermatomal herpes zoster, cytomegalovirus infections, BK virus infection, and listeriosis were reported with TOCINIB. Some patients have presented with disseminated rather than localized disease, and were often taking concomitant immunomodulating agents such as methotrexate. Or corticosteroids.
In the UC population, TOCINIB treatment with 10 mg twice daily was associated with greater risk of serious infections compared to 5 mg twice daily. Additionally, opportunistic herpes zoster infections (including meningoencephalitis, ophthalmologic, and disseminated cutaneous) were, seen in patients who were treated with TOCINIB 10 mg twice daily. Other serious infections that were not reported in clinical studies may also occur (e.g., coccidioidomycosis).
Avoid use of TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER in patients with an active, serious infection, including localized infections. The risks and benefits of treatment should be considered prior to initiating TOCINIB/TOCINIB ER in patients:
– with chronic or recurrent infection
– who have been exposed to tuberculosis
– with a history of a serious or an opportunistic infection
– who have resided or traveled in areas of endemic tuberculosis or endemic mycoses; or
– with underlying conditions that may predispose them to infection.
Patients should be closely monitored for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment with TOCINIB/TOCINIB ER. TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER should be interrupted if a patient develops a serious infection, an opportunistic infection, or sepsis. A patient who develops a new infection during treatment with TOCINIB/TOCINIB ER should undergo prompt and complete diagnostic testing appropriate for an immunocompromised patient; appropriate antimicrobial therapy should be initiated, and the patient should be closely monitored.,
Caution is also recommended in patients with a history of chronic lung disease, or in those who develop interstitial lung disease, as they may be more prone to infections.
Risk of infection may be higher with increasing degrees of lymphopenia and consideration should be given to lymphocyte counts when assessing individual patient risk of infection. Discontinuation and monitoring criteria for lymphopenia are recommended.
Tuberculosis
Patients should be evaluated and tested for latent or active infection prior to and per applicable guidelines during administration of TOCINIB/TOCINIB ER. Anti-tuberculosis therapy should also be considered prior to administration of TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER in patients with a past history of latent or active tuberculosis in whom an adequate course of treatment cannot be confirmed, and for patients with a negative test for latent tuberculosis but who have risk factors for tuberculosis infection. Consultation with a physician with expertise in the treatment of tuberculosis is recommended to aid in the decision about whether initiating anti-tuberculosis therapy is appropriate for an individual patient.
Patients should be closely monitored for the development of signs and symptoms of tuberculosis, including patients who tested negative for latent tuberculosis infection prior to initiating therapy.
Patients with latent tuberculosis should be treated with standard antimycobacterial therapy before administering TOCINIB/TOCINIB ER.
Viral Reactivation
Viral reactivation, including cases of herpes virus reactivation (e.g., herpes zoster), were observed in clinical studies with TOCINIB. The impact of TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER on chronic viral hepatitis reactivation is unknown Patients who screened positive for hepatitis B or C were excluded from clinical trials. Screening for viral hepatitis should be performed in accordance with clinical guidelines before starting therapy with TOCINIB/TOCINIB ER.
Malignancy and Lymphoproliferative Disorders
Consider the risks and benefits of TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER treatment prior to initiating therapy in patients with a known malignancy other than a successfully treated non-melanoma skin cancer(NMSC) or when considering continuing TOCINIB)TOCINIB ER in patients who develop a malignancy Malignancies were observed in clinical studies of TOCINIB.
Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer
Non-melanoma skin cancers (NMSCs) have been reported in patients treated with TOCINIB. Periodic skin examination is recommended for patients who are at increased risk for skin cancer. In the UC population; treatment with TOCINIB 10 mg twice daily was associated with greater risk of NMSC.
5.2 Gastrointestinal Perforations
Events of gastrointestinal perforation have been reported in clinical studies with Tofacitinib, although the role of JAK inhibition in these events is not known. In these studies, many patients with rheumatoid arthritis were receiving background therapy with Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs(NSAIDs).
There was no discernable difference in frequency of gastrointestinal perforation between the placebo and the Tofacitinib arms in clinical trials of patients with UC, and many of them were receiving background corticosteroids.
TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER should be used with caution in patients who may be at increased risk for gastrointestinal perforation (e.g., patients with a history of diverticulitis or taking NSAIDs)’ Patients presenting with new onset abdominal symptoms should be evaluated promptly for early identification of gastrointestinal perforation
5.3 Laboratory Abnormalities
Lymphocyte Abnormalities
Treatment with TOCINIB was associated with initial lymphocytosis at one month of exposure followed by a gradual decrease in mean absolute lymphocyte counts below the baseline of approximately 10% during 12 months of therapy. Lymphocyte counts less than 500 cells/mm² were associated with an increased incidence of treated and serious infections.
Avoid initiation of TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER treatment in patients with a low lymphocyte count (i.e., less than 500 cells/mm’). In patients who develop a confirmed absolute lymphocyte count less than 500 cells/mm², treatment with TOCINIB/TOCINIB ER is not recommended.
Monitor lymphocyte counts at baseline and every 3 months thereafter. For recommended modifications based on lymphocyte counts.
Neutropenia
Treatment with TOCINIB was associated with an increased incidence of neutropenia (less than2000 cells/mm’)compared to placebo.
Avoid initiation of TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER treatment in patients with a low neutrophil count (i.e., ANC less than 1000 cells/mm),For patents who develop a persistent ANC of 500 to 1000 cells/mm², interrupt TOCINIB / TOCINIB ER dosing until ANC is greater than or equal to 1000 cells/mm?. In patients who develop an ANC less than 500 cells/mm², treatment with
TOCINIB/TOCINIB ER is not recommended.
Monitor neutrophil counts at baseline and after 4-8 weeks of treatment and every 3 months thereafter. For recommended modifications based on ANC results.
Anemia
Avoid initiation of TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER treatment in patients with a low hemoglobin level (i.e., less than 9 g/dL). Treatment with TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER should be interrupted in patients who develop hemoglobin levels less than 8g/dL or whose hemoglobin level drops greater than 2 g/dL on treatment.
Monitor hemoglobin at baseline and after 4-8 weeks of treatment and every 3 months thereafter. For recommended modifications based on hemoglobin results.
Liver Enzyme Elevations
Treatment with TOCINIB was associated with an increased incidence of liver enzyme elevation compared to placebo. Most of these abnormalities occurred in studies with background DMARD (primarily methotrexate) therapy. Routine monitoring of liver tests and prompt investigation of the causes of liver enzyme elevations is recommended to identify potential cases of drug induced liver injury. If drug-induced liver injury is suspected, the administration of TOCINIB/TOCINIB ER should be interrupted until this diagnosis has been excluded.
Lipid Elevations
Treatment with TOCINIB was associated with dose-dependent increases in lipid parameters including total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. Maximum effects were generally observed within 6 weeks. There were no clinically relevant changes in LDL/HDL cholesterol ratios. The effect of these lipid parameter elevations on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality has not been determined. Assessment of lipid parameters should be performed ‘approximately 4-8 weeks following initiation of TOCINIB/TOCINIB ER therapy.
5.4 Vaccinations
Avoid use of live vaccines concurrently with TOCINIB/TOCINIB ER. The interval between live vaccinations and initiation of tofacitinib therapy should be in accordance with current vaccination guidelines regarding immunosuppressive agents.
5.5 Risk of Gastrointestinal Obstruction with a Non-Deformable
Extended-Release Formulation such as TOCINIB ER
As with any other non-deformable material, caution should be used when administering TOCINIB ER to patients with pre-existing severe gastrointestinal narrowing (pathologic or iatrogenic). There have been rare reports of obstructive symptoms in patients with known strictures in association with the ingestion of other drugs utilizing a non-deformable extended-release formulation.
6. ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
– Serious Infections
– Malignancy and Lymphoproliferative Disorders
– Gastrointestinal Perforations
– Laboratory Abnormalities
6.1 Side Effects
Common or Very Common; Anemia, cough, diarrhoea, fatigue, fever, gastrointestinal discomfort, gastrointestinal disorders, headache, hypertension, increased risk of infection, joint disorders, nausea, peripheral oedema, skin reactions, vomiting.
Uncommon: Decreased Leucocytes, Deep vein thrombosis (discontinue permanently), dehydration, dyslipidaemia, dyspnoea, hepatic steatosis, insomnia, ligament sprain, muscle strain, musculoskeletal pain, neoplasms, neutropenia, paraesthesia, pulmonary embolism (discontinue permanently), sinus congestion, tendinitis, venous thromboembolism (discontinue permanently), weigh increased
Rare or Very Rare: Meningitis cryptococcal, sepsis
Frequency not known: Angioedema, BK virus infection, interstitial. lung disease (including fatal cases), malignancy, reactivation of infections
7. DRUGINTERACTIONS
Table 3 includes drugs with clinically important drug interactions when administered concomitantly with TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER and instructions for preventing or managing them.
Table 3: Clinical Relevant Interactions Affecting TOCINIB and TOCINIB ER When Coadministered with Other Drugs
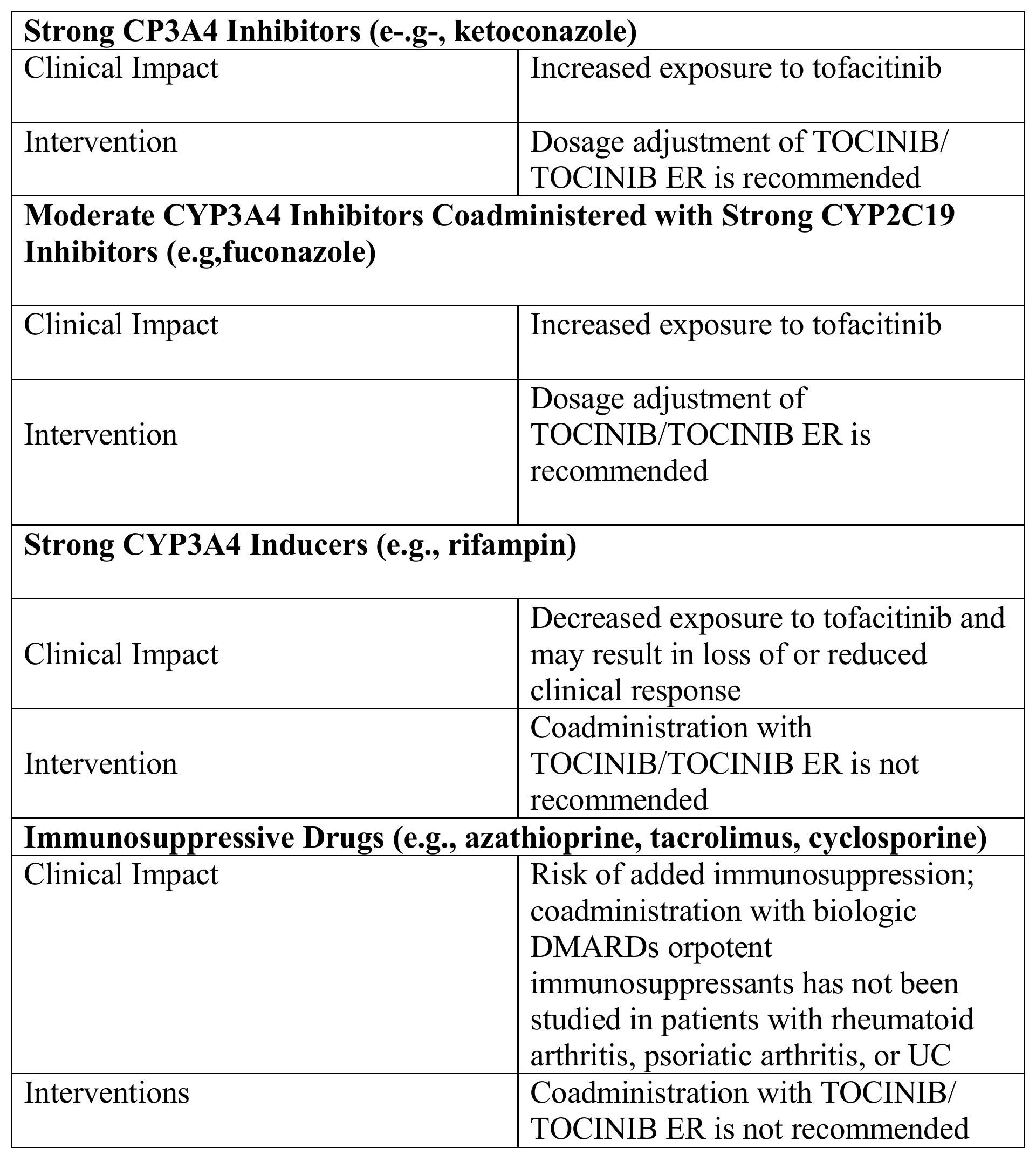
8.USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data with TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER use in pregnant women are insufficient to establish a drug associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. There are risks to the mother and the fetus: associated with rheumatoid arthritis and UC in pregnancy. In animal reproduction studies, fetocidal and teratogenic effects were noted when pregnant rats and rabbits received tofacitinib during the period of organogenesis at exposures multiples of 73-times and 6.3-times the maximum recommended dose of 10 mg twice daily, respectively. Further, in a peri and post-natal study in rats, tofacitinib resulted in reductions in live litter size, Postnatal survival, and pup body weights at exposure multiples of approximately 73-times the recommended dose of 5 mg twice daily and approximately 36 times the maximum recommended dose of 10 mg twice daily, respectively.
The estimated background risks of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations are unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
Published data suggest that increased disease activity is associated with the risk of developing adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with rheumatoid arthritis or ulcerative colitis. Adverse pregnancy outcomes include preterm delivery (before 37 weeks of gestation), low, birth weight (less than 2500 g) infants, and small for gestational age at birth.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of tofacitinib in human milk; the effects on a breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production: Tofacitinib is present in the milk of lactating rats. When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely that the drug will be present in human milk. Given the serious adverse reactions seen in adults treated with TOCINIB/TOCINIB ER, such as increased risk of serious infections, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment and for at least 18 hours after the last dose of TOCINIB or 36 hours after the last dose of TOCINIB ER (approximately 6elimination half-lives).
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Females
In an animal reproduction study, tofacitinib at AUC multiples of-13 times the recommended dose of 5:mg twice daily and 6.3 times the. maximum recommended dose of-10. mg twice daily demonstrated adverse embryo-fetal findings. However, there is uncertainty as to how these animal findings relate to females of reproductive potential treated with the recommended clinical dose. Consider pregnancy planning and prevention for females of reproductive potential.
Infertility
Females
Based on findings in rats, treatment with TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER may result in reduced fertility in females of reproductive potential. It is not known if this effect is reversible.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safely and effectiveness of TOCINIB/-TOCINIB ER in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
As there is a higher incidence of infections in the elderly population in general,
caution should be used when treating the elderly.
8.6 Use in Diabetics
As there is a higher incidence of infection in diabetic population in general caution should be used when treating patients with diabetes.
8.7 Renal Impairment
Moderate and Severe Impairment
TOCINIB-treated patients with moderate or severe renal impairment had greater tofacitinib blood concentrations than TOCINIB-treated patients with normal renal function. Therefore, dosage adjustment of TOCINIB is recommended in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment.
– Rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis patients with moderate or severe renal impairment receiving TOCINIB ER should switch to TOCINIB and adjust the dosage.
Mild impairment
No dosage adjustment is required in patients with mild renal impairment.
8.8 Hepatic Impairment
Severe Impairment
TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment; therefore, use of TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER in patients with severe hepatic impairment is not recommended.
Moderate Impairment
TOCINIB-treated patients with moderate hepatic impairment had greater tofacitinib blood concentration than TOCINIB-treated, patients with normal hepatic function. Higher blood concentrations may increase the risk of some adverse reactions. Therefore, dosage adjustment of TOCINIB is recommended in patients with moderate, hepatic impairment.
– Rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis patients receiving TOCINIB ER should switch to TOCINIB and adjust the dosage.
Mild Impairment
No dosage adjustment of TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER is required in patients with mild hepatic impairment.
Hepatitis B or C Serology
The safety and efficacy of TOCINIB/ TOCINIB ER have not been studied in patients with positive hepatitis B virus or hepatitis C virus serology.
9. OVERDOSAGE
There is no specific antidote for overdose with TOCINIB/TOCINIB ER. In case of an overdose, it is recommended that the patient be monitored for signs and symptoms of adverse reactions.
10. STORAGE
Store below 30’C and protect from light.
11.PRESENTATION
Alu-Alu Blister pack of 3 x 10’s in a carton along with pack insert.
KEEP MEDICINE OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.