Fineron 10 / 20
- ENG
- မြန်မာ
For the use of Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or Laboratory
Finerenone Tablets 10 mg
FINERON 10
Composition
Each film-coated tablet contains:
Finerenone ……….. 10 mg
Finerenone Tablets 20 mg
FINERON 20
Composition
Each film-coated tablet contains:
Finerenone ……. 20 mg
CLINICAL PARTICULARS
Therapeutic indications
Finerenone is indicated for the treatment of chronic kidney disease (with albuminuria) associated with type 2 diabetes in adults.
Posology and method of administration
Posology
The recommended target dose is 20 mg finerenone once daily.
The maximum recommended dose is 20 mg finerenone once daily.
Initiation of treatment
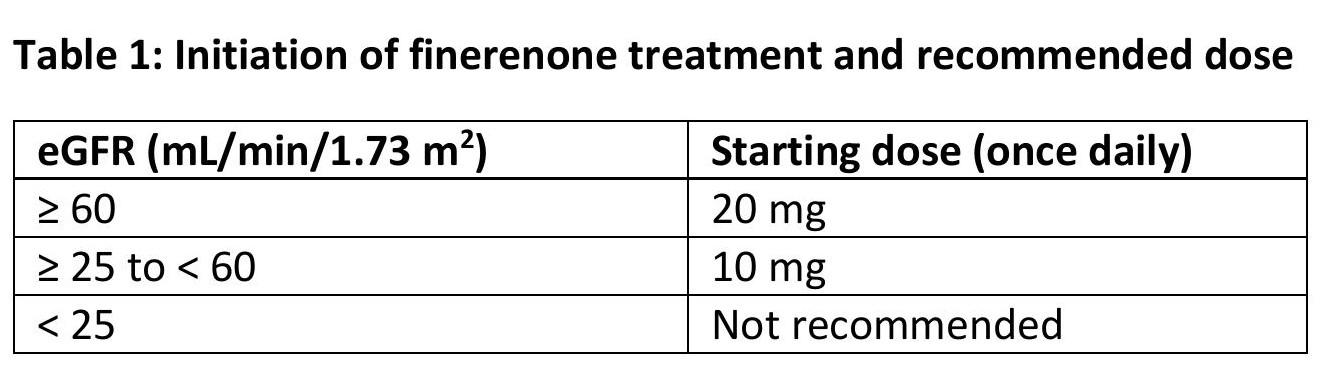
Serum potassium and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) have to be measured to determine if finerenone treatment can be initiated and to determine the starting dose.
If serum potassium ≤ 4.8 mmol/L, finerenone treatment can be initiated. For monitoring of serum potassium, see below ‘Continuation of treatment’.
If serum potassium > 4.8 to 5.0 mmol/L, initiation of finerenone treatment may be considered with additional serum potassium monitoring within the first 4 weeks based on patient characteristics and serum potassium levels.
If serum potassium>5.0 mmol/L, finerenone treatment should not be initiated.
The recommended starting dose of finerenone is based on eGFR and is presented in table 1.
Continuation of treatment
Serum potassium and eGFR have to be remeasured 4 weeks after initiation or re-start of finerenone treatment or increase in dose.
Thereafter, serum potassium has to be remeasured periodically and as needed based on patient characteristics and serum potassium levels.
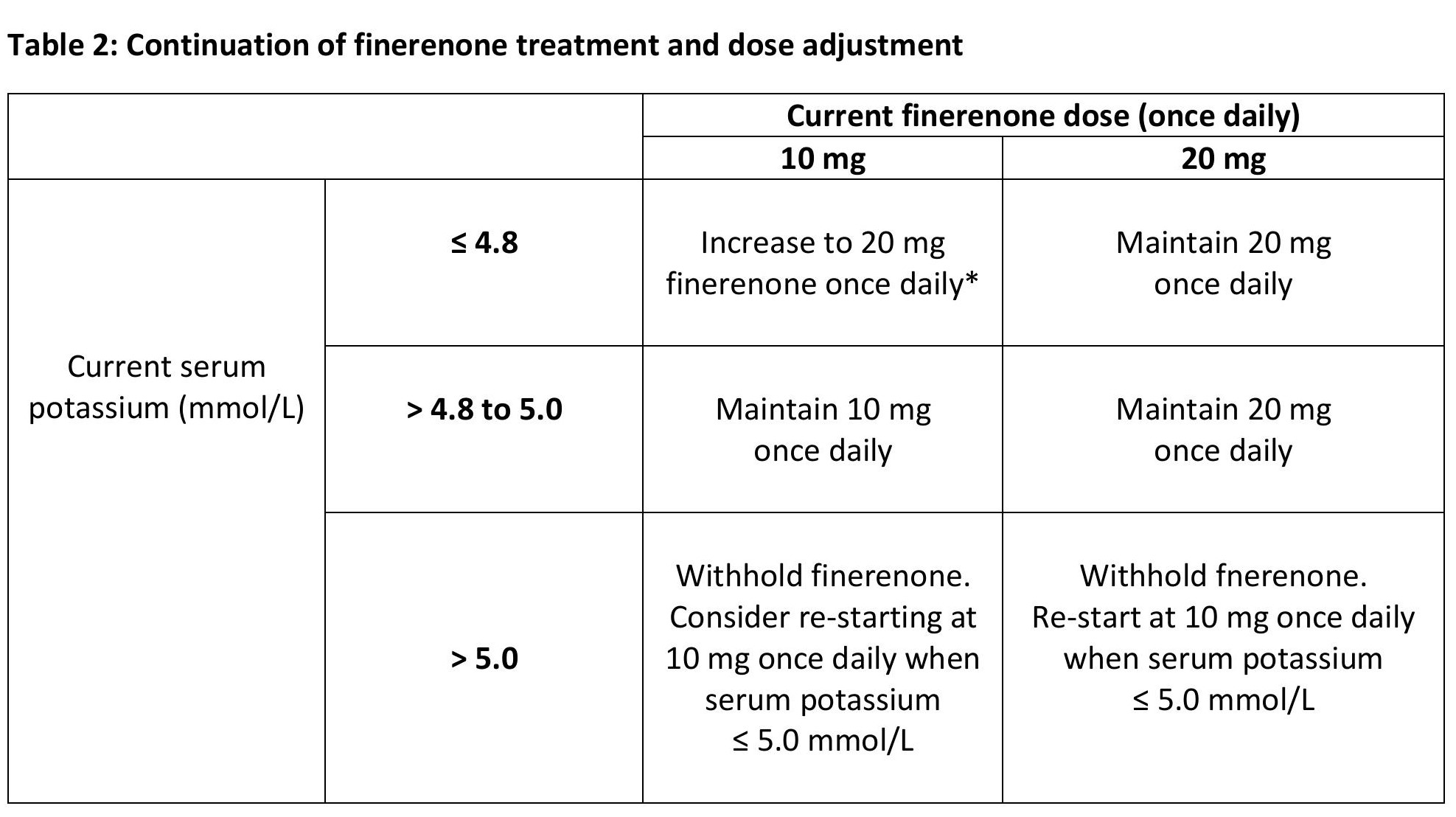
* maintain 10 mg once daily, if eGFR has decreased > 30% compared to the previous measurement
Missed dose
A missed dose should be taken as soon as the patient notices, but only on the same day. The patient should not take 2 doses to make up for a missed dose.
Special populations
Elderly
No dose adjustment is necessary in elderly patients.
Renal impairment
Initiation of treatment
In patients with eGFR < 25 mL/min/1.73 m, finerenone treatment should not be initiated due to limited clinical data.
Continuation of treatment
In patients with eGFR 2 15 mL/min/1.73 m, finerenone treatment can be continued with dose adjustment based on serum potassium, eGFR should be measured 4 weeks after initiation to determine whether the starting dose can be increased to the recommended daily dose of20 mg.
Due to limited clinical data, finerenone treatment should be discontinued in patients who have progressed to end-stage renal disease (eGFR < 15mL/min/1.73m2).
Hepatic impairment
Patients with
– Severe hepatic impairment:
Finerenone should not be initiated. No data are available.
– Moderate hepatic impairment:
No initial dose adjustment is required. Consider additional serum potassium monitoring and adapt monitoring according to patient characteristics.
– Mild hepatic impairment:
No initial dose adjustment is required.
Concomitant medication
In patients taking finerenone concomitantly with moderate or weak CYP3A4 inhibitors, potassium supplements trimethoprim, or trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, additional serum potassium monitoring and adaptation of monitoring according to patient characteristics should be considered.
Finerenone treatment decisions should be made as directed in table 2. Temporary discontinuation of finerenone may be necessary, when patients have to take trimethoprim, or trimethoprim /sulfamethoxazole.
Body weight
No dose adjustment is necessary based on body weight.
Paediatric population
The safety and efficacy of finerenone in children and adolescents aged under 18 years have not yet been established. No data are available.
Method of administration
Oral use
Tablets may be taken with a glass of water and with or without food. Tablets should not be taken with grapefruit or grape fruit juice.
Crushing of tablets
For patients who are unable to swallow whole tablets Finerenone tablets may be crushed and mixed with water or soft foods, such as apple sauce, directly before oral use.
Contraindications
– Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
– Concomitant treatment with strong inhibitors of CYP3A4,
e.g.,
– Itraconazole
– Ketoconazole
– Ritonavir
– Nelfinavir
– Cobicistat
– Clarithromycin
– Telithromycin
– Nefazodone
– Addison’s disease
Special warnings and precautions for use
Hyperkalaemia
Hyperkalaemia has been observed in patients treated with finerenone. Some patients are at a higher risk to develop hyperkalaemia. Risk factors include low eGFR, higher serum potassium and previous episodes of hyperkalaemia. In these patients more frequent monitoring has to be considered.
Initiation and continuation of treatment
If serum potassium > 5.0 mmol/L, finerenone treatment should not be initiated.
If serum potassium > 4.8 to 5.0 mmol/L, initiation of finerenone treatment may be considered with additional serum potassium monitoring, within the first 4 weeks based on patient characteristics and serum potassium levels.
If serum potassium > 5.0 mmol/L, finerenone treatment has to be withheld. Local guidelines for the management of hyperkalaemia have to be followed. Once serum potassium 5.0 mmol/L, finerenone treatment can be restarted at 10 mg once daily.
Monitoring
Serum potassium and eGFR have to be remeasured in al patients 4 weeks after initiation, re-start or increase in dose of finerenone. Thereafter, serum potassium has to be assessed periodically and as needed based on patient characteristics and serum potassium levels.
Concomitant medications
The risk of hyperkalaemia also may increase with the intake of concomitant medications that may increase serum potassium.
Finerenone should not be given concomitantly with
– Potassium-sparing diuretics (e.g., amiloride, triamterene) and
– Other mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs), e.g., eplerenone, esaxerenone, spironolactone, canrenone.
Finerenone should be used with caution and serum potassium should be monitored when taken concomitantly with
– Potassium supplements
Trimethoprim, or trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole.
Temporary discontinuation of finerenone may be necessary.
Renal impairment
The risk of hyperkalaemia increases with decreasing renal function. Ongoing monitoring of renal. function should be performed as needed according to standard practice.
Initiation of treatment
Finerenone treatment should not be initiated in patients with eGFR < 25mL/min/1.73 m2 as clinical data are limited.
Continuation of treatment
Due to limited clinical data, finerenone treatment should be discontinued in patients who have progressed to end-stage renal disease (eGFR < 15mL/min/1.73m2)
Hepatic impairment
Finerenone treatment should not be initiated in patients with severe hepatic impairment. These patients have not been studied but a significant increase in finerenone exposure is expected.
The use of finerenone in patients with moderate hepatic impairment may require additional monitoring due to an increase in finerenone exposure. Additional serum potassium monitoring and adaptation of monitoring have to be considered according to patient characteristics.
Heart failure
Patients with diagnosed heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and New York Heart Association II-IV were excluded from the phase Ill clinical studies.
Concomitant use of substances that affect finerenone exposure
Moderate and weak CYP3A4 inhibitors
Serum potassium should be monitored during concomitant use of finerenone with moderate or weak CYP3A4 inhibitors.
Strong and moderate CYP3A4 inducers
Finerenone should not be used concomitantly with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers.
Grapefruit
Grapefruit or grapefruit juice should not be consumed during finerenone treatment.
Embryo-foetal toxicity
Finerenone should not be used during pregnancy unless there has been careful consideration of the benefit for the mother and the risk to the foetus. If a woman becomes pregnant while taking finerenone, she should be informed of potential risks to the foetus.
Women of childbearing potential should be advised to use effective contraception during treatment with finerenone.
Women should be advised not to breast-feed during treatment with finerenone.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Interaction studies have only been performed in adults.
Finerenone is cleared almost exclusively via cytochrome P450 (CYP)-mediated oxidative metabolism (mainly CYP3A4 [90%] with a small contribution of CYP2C8 [10%]).
Concomitant use contraindicated
Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors
Concomitant use of Finerenone with itraconazole clarithromycin and other strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g. ketoconazole, ritonavir, nelfinavir, cobicistat, telithromycin or nefazodone) is contraindicated, since a marked increase in finerenone exposure is expected.
Concomitant use not recommended
Strong and moderate CYP3A4 inducers
Finerenone should not be used concomitantly with rifampicin and other strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital, St John’s Wort) or with efavirenz and other moderate CYP3A4 inducers. These CYP3A4 inducers are expected to markedly decrease finerenone plasma concentration and result in reduced therapeutic effect.
Certain medicinal products that increase serum potassium
Finerenone should not be used concomitantly with potassium-sparing diuretics (e.g., amiloride, triamterene) and other MRAs (e.g., eplerenone, esaxerenone, spironolactone, canrenone). It is anticipated that these medicinal products increase the risk for hyperkalaemia.
Grapefruit
Grapefruit or grapefruit juice should not be consumed during finerenone treatment, as it is expected to increase the plasma concentrations of finerenone through inhibition of CYP3A4.
Concomitant use with precautions
Moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors
In a clinical study, concomitant use of erythromycin (500 mg three times a day)led to a 3.5-fold increase in finerenone AUC and 1.9-fold increase in its C In another clinical study verapamil (240 mg controlled-release tablet once daily) led to a 2.7- and 2.2-fold increase in finerenone AUC and Cmax’ respectively.
Serum potassium may increase, and therefore, monitoring of serum potassium.is recommended, especially during initiation or changes to dosing of finerenone or the CYP3A4 inhibitor.
Weak CYP3A4 inhibitors
The physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK simulations suggest that fluvoxamine (100 mg twice daily) increases finerenone AUC (1.6-fold) and Cmax(1.4-fold)
Serum potassium may increase, and therefore, monitoring of serum potassium is recommended, especially during initiation or changes to dosing of finerenone or the CYP3A4 inhibitor.
Certain medicinal products that increase serum potassium
Concomitant use of Finerenone with potassium supplements and trimethoprim, or trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole is anticipated to increase the risk of hyperkalaemia. Monitoring of serum potassium is required.
Temporary discontinuation of Finerenone during trimethoprim, or trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole treatment may be necessary.
Antihypertensive medicinal products
The risk for hypotension increases with concomitant use of multiple other antihypertensive medicinal products. In these patients, blood pressure monitoring is recommended.
Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
Contraception in females
Women of childbearing potential should use effective contraception during finerenone treatment.
Pregnancy
There are no data from the use of finerenone in pregnant women. Studies in animals have shown reproductive toxicity.
Finerenone should not be used during pregnancy unless the clinical condition of the woman requires treatment with finerenone. If the woman becomes pregnant while taking finerenone, she should be informed of potential risks to the foetus.
Breast-feeding
It is unknown whether finerenone/metabolites are excreted in human milk.
Available pharmacokinetic/toxicological data in animals have shown excretion of finerenone and its metabolites in milk. Rat pups exposed via this route showed adverse reactions.
A risk to the newborns/infants cannot be excluded.
A decision must be made whether to discontinue breast-feeding or to discontinue/abstain from Finerenone therapy taking into account the benefit of breast-feeding for the child and the benefit of therapy for the woman.
Fertility
There are no data on the effect of finerenone on human fertility.
Animal studies have shown impaired female fertility at exposures considered in excess to the maximum human exposure, indicating low clinical relevance.
Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Finerenone has no influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
Undesirable effects
Summary of the safety profile
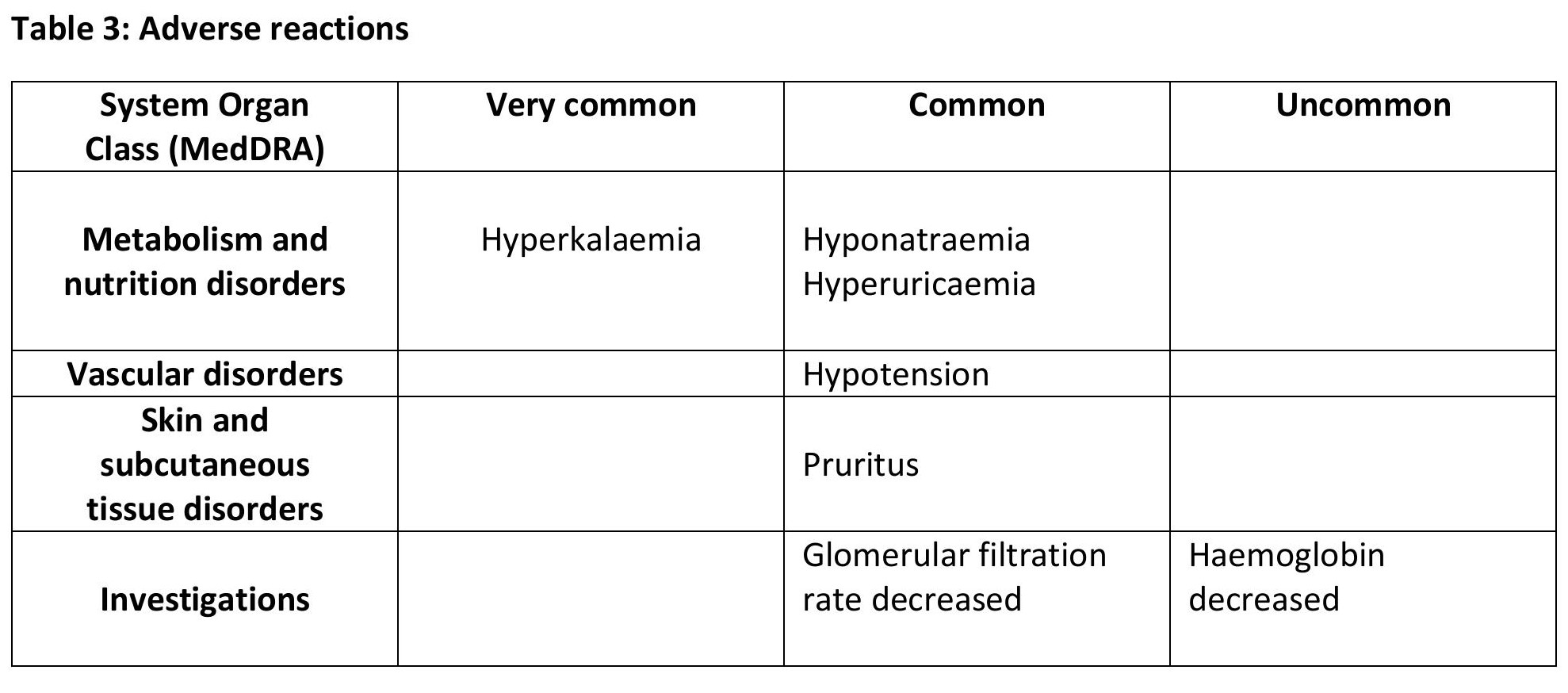
The most frequently reported adverse reaction under treatment with finerenone was hyperkalaemia (14.0%).
Tabulated list of adverse reactions
The adverse reactions observed are listed in table 3. They are classified according to MedDRA system organ class database and frequency convention.
Adverse reactions are grouped according to their frequencies in the order of decreasing seriousness. Frequencies are defined, as follows:
Very common (≥ 1/10), common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10), uncommon (21/1,000to<1/100), rare (1/10,000 to < 1/1,000), very rare (< 1/10,000),not known (cannot be estimated from the available data).
Overdose
The most likely manifestation of overdose is anticipated to be hyperkalaemia. If hyperkalaemia develops, standard treatment should be initiated.
Finerenone is unlikely to be efficiently removed by haemodialysis given its fraction bound to plasma proteins of about 90%.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
Mechanism of Action
Pharmacotherapeutic group: diuretics, aldosterone antagonists, ATC code: C03DA05
Finerenone is a nonsteroidal, selective antagonist of the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) which is activated by aldosterone and cortisol and regulates gene transcription. Its binding to the MR leads to a specific receptor-ligand complex that blocks recruitment of transcriptional coactivators implicated in the expression of pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic mediators.
Preclinical safety data
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety pharmacology, single dose toxicity, repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity, phototoxicity, carcinogenic potential and male and female fertility.
STORAGE
Store below 30°C and protect from light.
PRESENTATION
Alu-Alu Blister pack of 3 x 10’s in a carton along with pack insert.
KEEP MEDICINE OUTOF REACH OF CHILDREN.
Product of:
Zifam Pinnacle Pty. Ltd.,
Sydney, Australia.
Manufactured by:
Zifam Pyrex Myanmar Co.Ltd.,
Lot C6, Zone A, Thilawa SEZ, Thanlyin &
Kyauk Tan Township, Yangon, Myanmar.