ZIDAPA 5/10
- ENG
- မြန်မာ

For the use of Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or Laboratory
Dapagliflozin Tablets 5 mg
ZIDAPA 5
COMPOSITION
Each film-coated tablet contains:
Dapagliflozin Propanediol
equivalent to Dapagliflozin …. 5 mg
Dapagliflozin Tablets 10 mg
ZIDAPA 10
COMPOSITION
Each film-coated tablet contains.
Dapagliflozin Propanediol
equivalent to Dapagliflozin …. 10 mg
DESCRIPTION
Dapagliflozin is described chemically as D-glucitol, 1, 5- anhydro-1-C-[4-chtoro-3- [(4ethoxyphenyl) methyl] phenyl]-, (1S)-, compounded with (2S)-1,2- propanediol, hydrate (1:1:1).
The empirical formula is C21H25CIO6 · C3H8O2· H2O and the molecular weight is 502.98.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2), expressed in the proximal renal tubules, is responsible for the majority of the reabsorption of filtered glucose from the tubular lumen.
Dapagliflozin is an inhibitor of SGLT2, By inhibiting SGLT2, dapagliflozin reduces reabsorption of filtered glucose and thereby promotes urinary glucose excretion. Dapagliflozin also reduces sodium reabsorption and increases the delivery of sodium to the distal tubule.
This may influence several physiological functions including, but not restricted to, lowering both pre-and afterload of the heart and downregulation of sympathetic activity, and decreased intraglomerular pressure which is believed to be mediated by increased tubuloglomerular feedback.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ZIDAPA is a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor indicated for:
- as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- to reduce the risk of hospitalization for heart failure in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus and either established cardiovascular disease or multiple cardiovascular risk factors.
- to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in adults with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (NYHA class II-IV).
- to reduce the risk of sustained eGFR decline, end stage kidney disease cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in adults with chronic kidney disease at risk of progression.
Limitations of use:
Not for treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus.
ZIDAPA is not recommended for use to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus with an eGFR less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m2. ZIDAPA is likely to be ineffective in this setting based upon its mechanism of action.
ZIDAPA is not recommended for the treatment of chronic kidney disease in patients with polycystic kidney disease or patients requiring or with a recent history of immunosuppressive therapy for the treatment of kidney disease.
ZIDAPA is not expected to be effective in these populations.
DOSAGEANDADMINISTRATION
Assess volume status and correct volume depletion before initiating.
See the following table for dosage recommendations based on estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).
| eGFR
(mL/min/1.73m2) |
Recommended Dose |
|
eGFR 45 or greater
|
To improve glycemic control, the
recommended starting eGFR 45 or dose is 5mg orally greater once daily. Dose can be increased to 10 mg orally once daily for additional glycemic control*. |
| For all other indications, the recommended
starting dose is 10 mg orally once daily. |
| eGFR 25 to less than 45 | 10 mg orally once daily*. |
|
eGFR less than 25
|
Initiation is not recommended however
patients may continue 10mg orally once daily to reduce the risk of eGFR decline, ESKD, CV death and hHF. |
*ZIDAPA is not recommended for use to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus with an eGFR less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m2.
ZIDAPA is likely to be ineffective in this setting based upon its mechanism of action. hHF: hospitalization for heart failure, CV: Cardiovascular, ESKD: End Stage Kidney Disease.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
. History of serious hypersensitivity reaction to ZIDAPA.
. Patients on dialysis
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Ketoacidosis in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus : Assess patients who present with signs and symptoms of metabolic acidosis for ketoacidosis regardless of blood glucose level. If suspected discontinue ZIDAPA, evaluate and treat promptly. Before initiating ZIDAPA, consider risk factors for ketoacidosis. Patients on ZIDAPA may require monitoring and temporary discontinuation of therapy in clinical situations known to predispose to ketoacidosis.
- Volume depletion : Before initiating ZIDAPA, assess volume status and renal function in the elderly, patients with renal impairment or low systolic blood pressure, and in patients on diuretics. Monitor for signs and symptoms during therapy.
- Urosepsis and Pyelonephritis : Evaluate for signs and symptoms of urinary tract infections and treat promptly, if indicated.
- Hypoglycemia : Consider a lower dose of insulin or the insulin secretagogue to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia when used in combination with ZIDAPA.
- Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Perineum (Fournier’s Gangrene) : Serious, lifethreatening cases have occurred in patients with diabetes, both females and males. Assess patients presenting with pain or tenderness, erythema, or swelling in the genital or perineal area, along with fever or malaise. If suspected, institute prompt treatment.
- Genital Mycotic Infections : Monitor and treat if indicated.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions, associated, with ZIDAPA (5% or greater incidence) were female genital, mycotic infections, nasopharyngitis, and urinary tract infections.
USE IN SPECIAL POPULATION
Pregnancy : Advise females of the potential risk to a fetus especially during the second and third trimesters.
Lactation : ZIDAPA is not recommended when breastfeeding.
Geriatrics : Higher incidence of adverse reactions related to hypotension.
Renal Impairment : Higher incidence of adverse reactions related to volume depletion.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
In Vitro Assessment of Drug Interactions
In in vitro studies, dapagliflozin and dapagliflozin 3-0-glucuronide neither inhibited CYP 1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6,or 3A4, nor induced CYP 1A2,2B6, or 3A4. Dapagliflozin is a weak substrate of the Pglycoprotein (P-gp) active transporter, and dapagliflozin 3-Oglucuronide is a substrate for the OAT3 active transporter. Dapagliflozin or dapagliflozin 3-O-glucuronide did not meaningfully inhibit P-gp, OCT2, OAT1, or OAT3 active transporters. Overall, dapagliflozin is unlikely to affect the pharmacokinetics of concurrently administered medications that are P-gp, OCT2, OAT1, or OAT3 substrates.
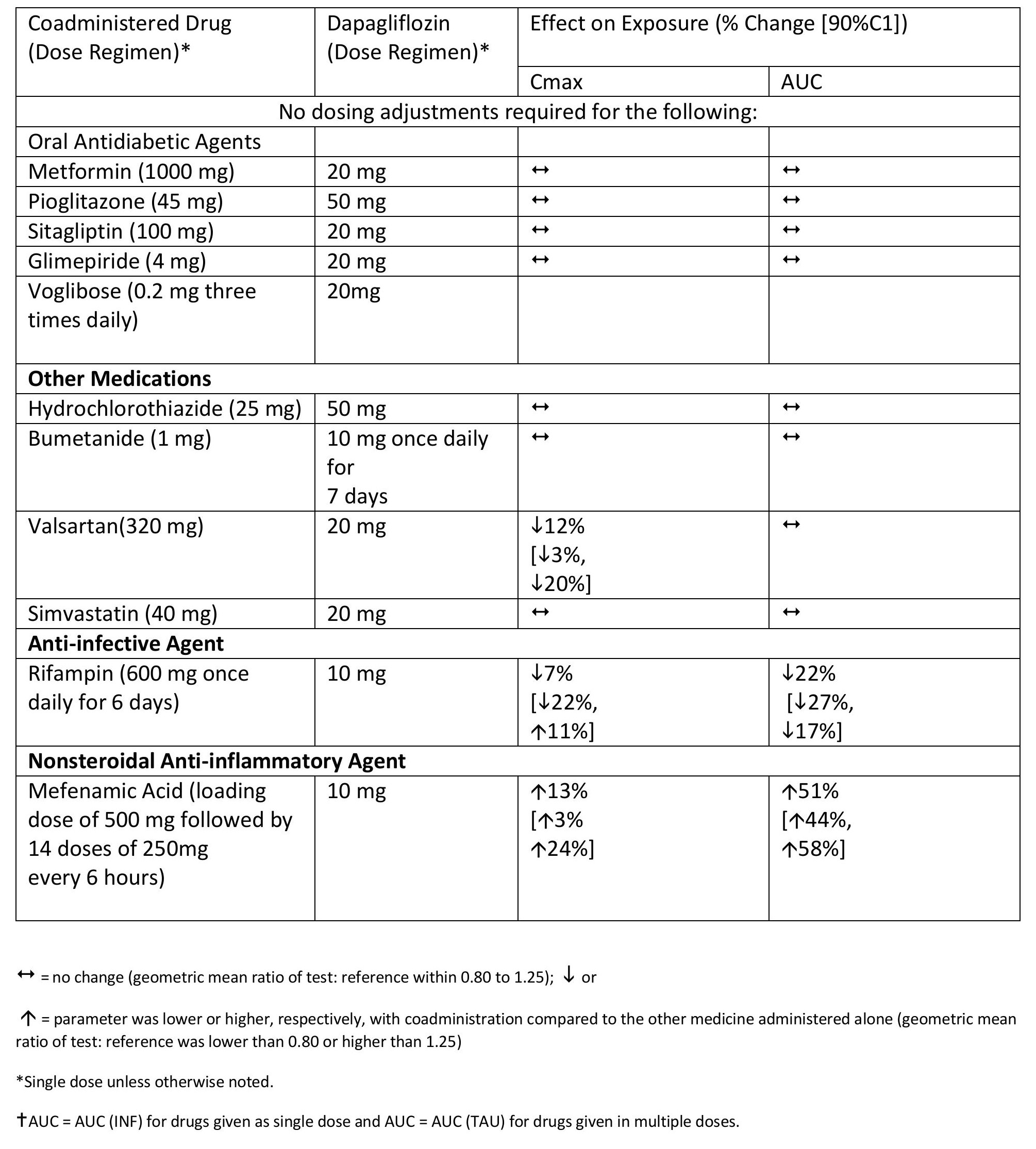
Effects of Other Drugs on Dapagliflozin
Effects of Coadministered Drugs on Dapagliflozin Systemic Exposure
No dose adjustments are recommended for dapagliflozin.
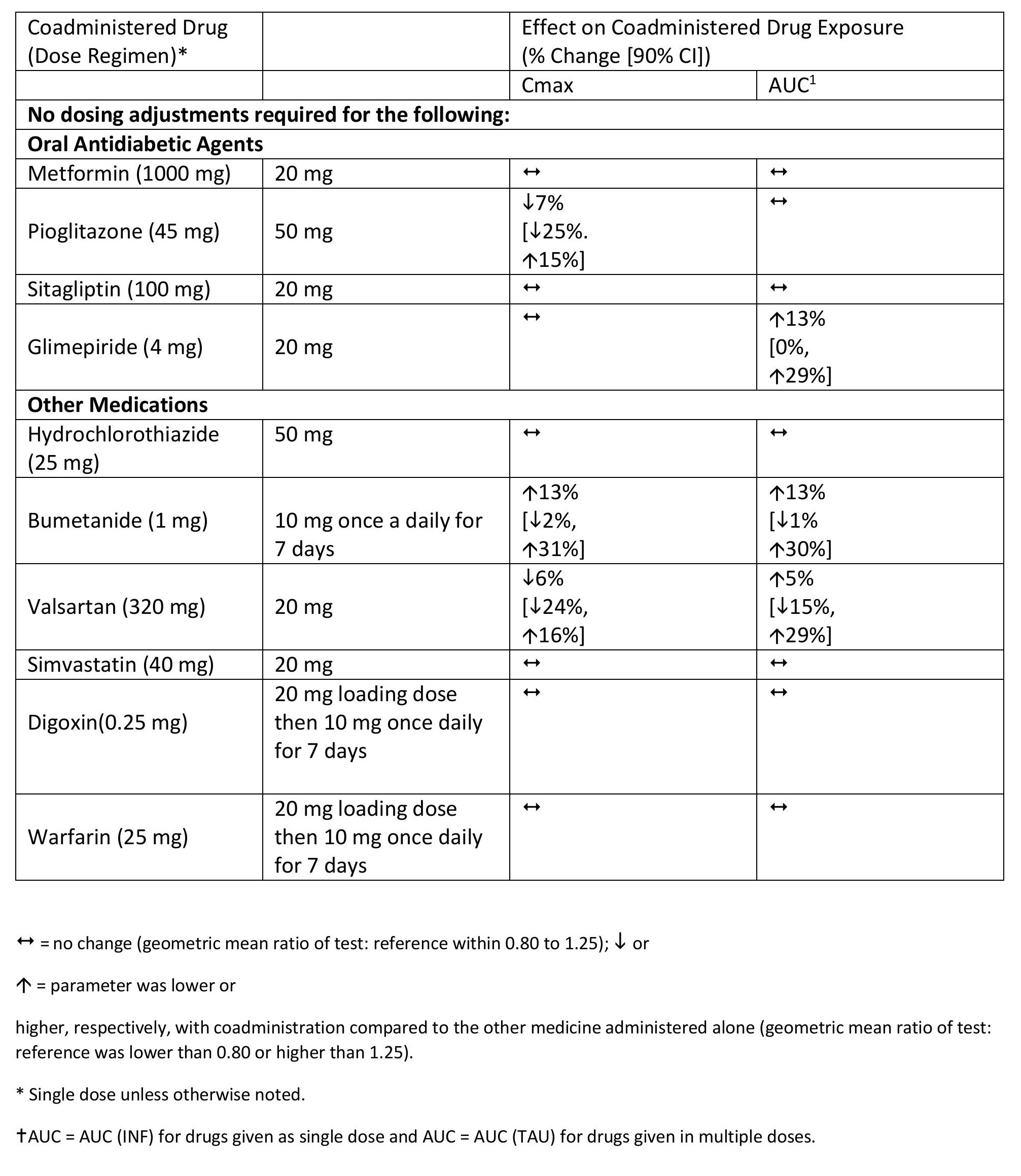
Effects of Dapagliflozin on the Systemic Exposures of Coadministered Drugs
STORAGE
Store below 30°C and protect from light.
PRESENTATION
Blister pack of 3 x 10’s in a carton box along with pack insert.
KEEP MEDICINE OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.